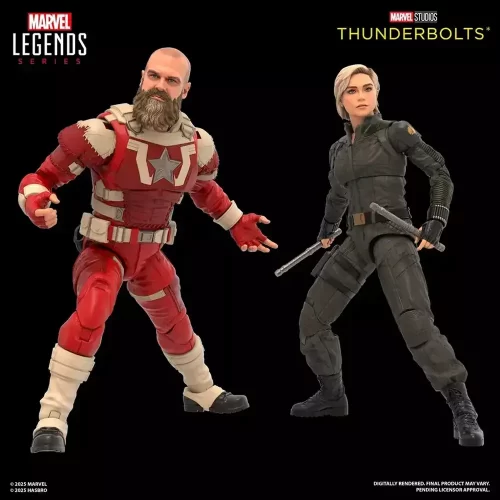
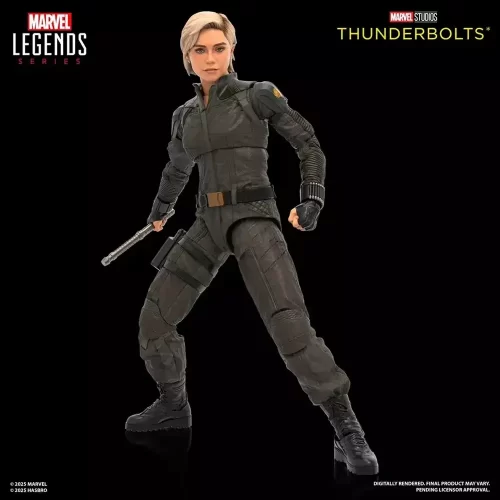
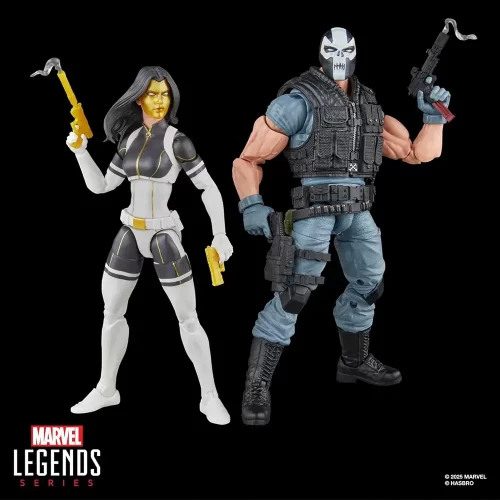
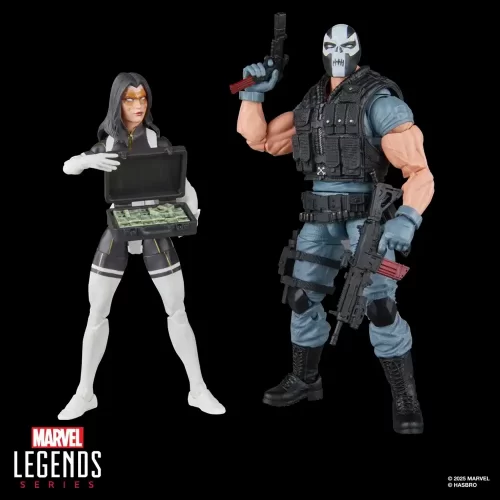
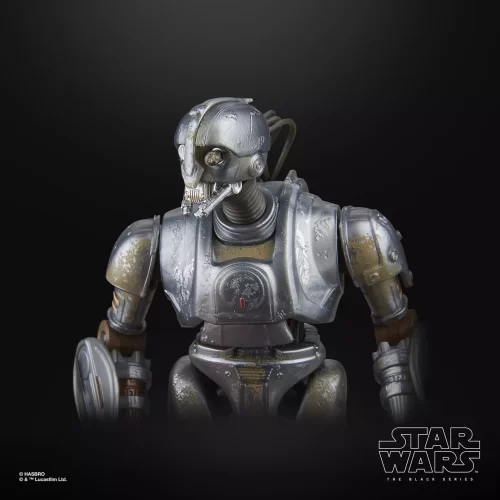
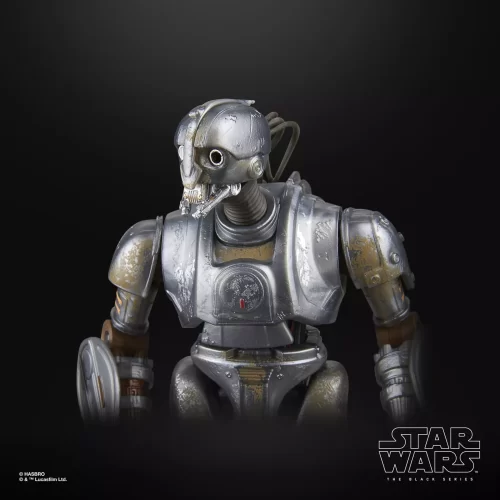
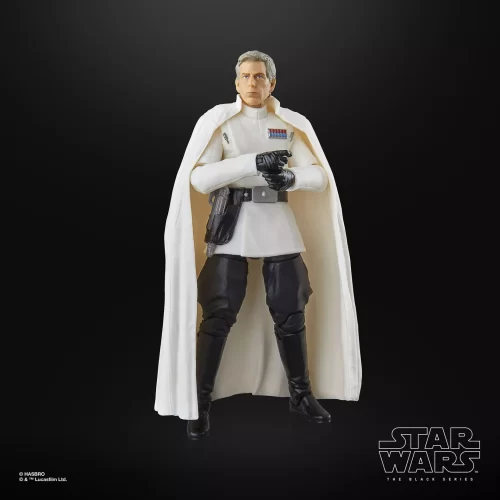
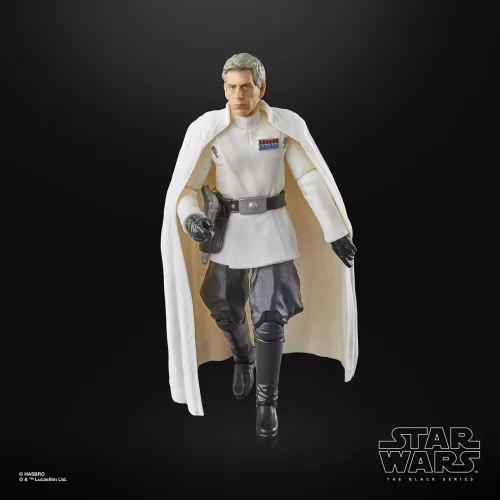
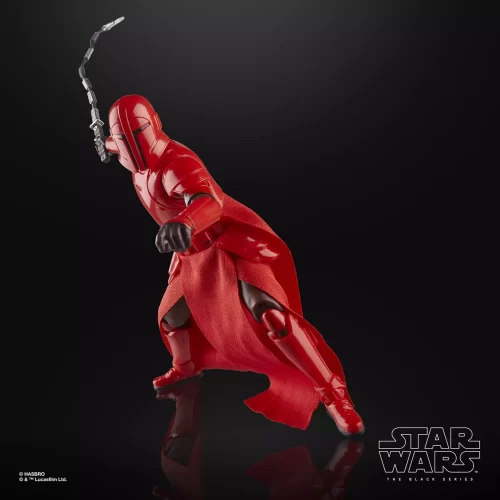
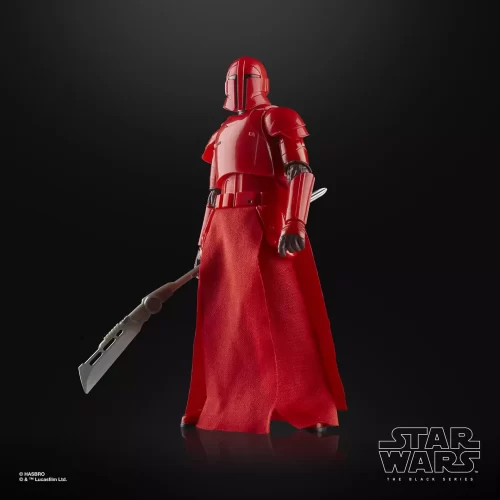
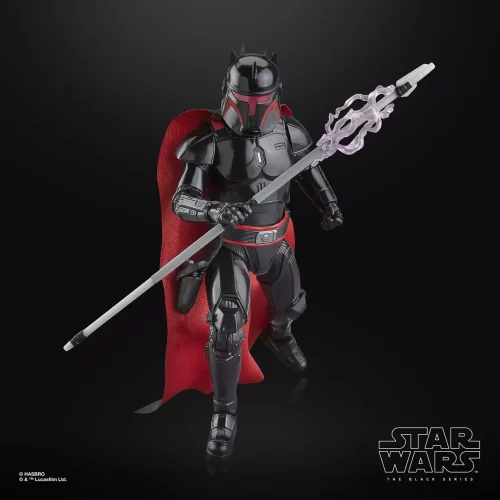
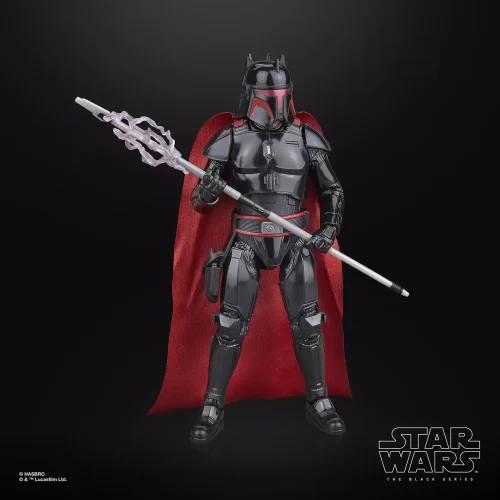
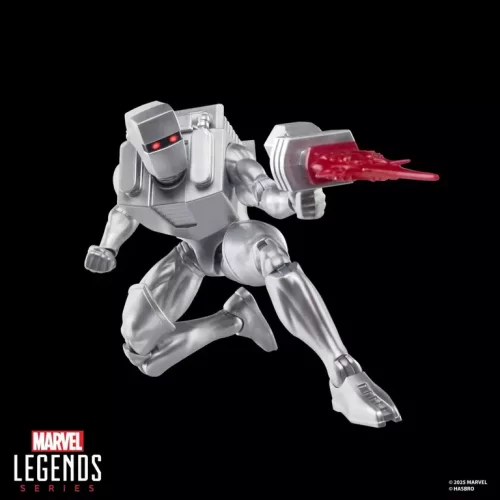
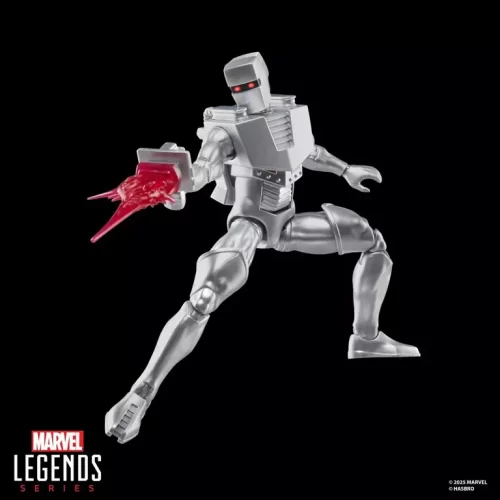
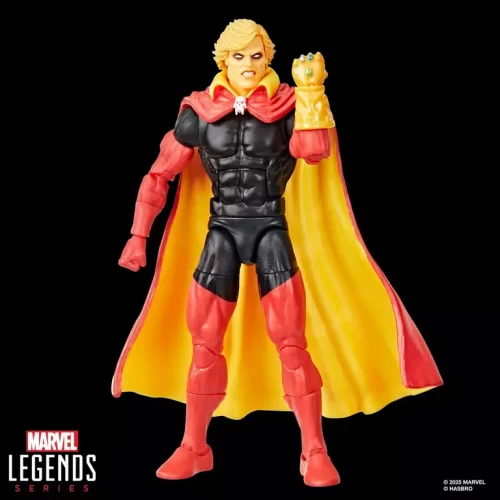
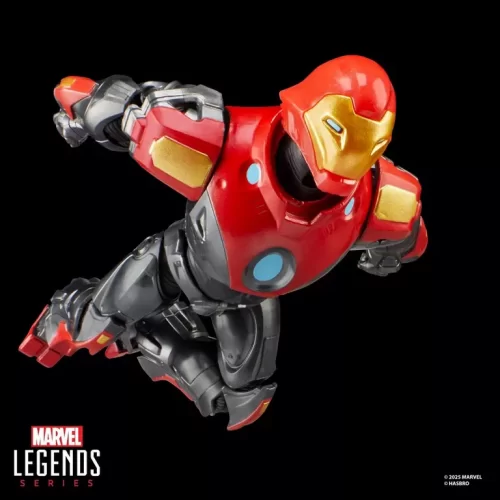
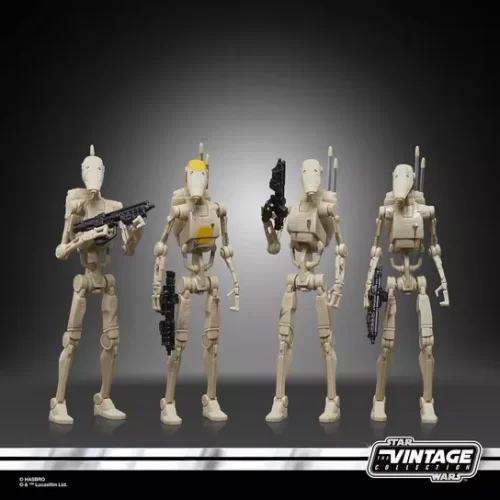
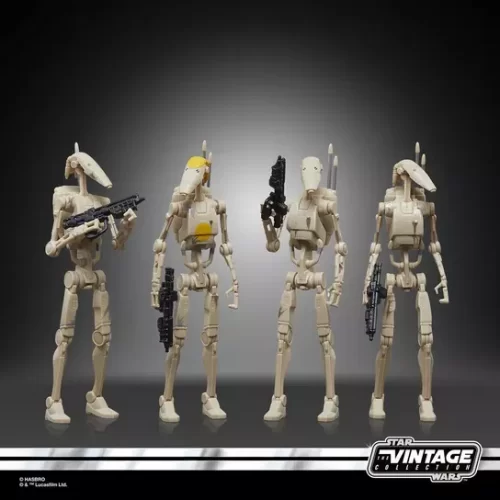
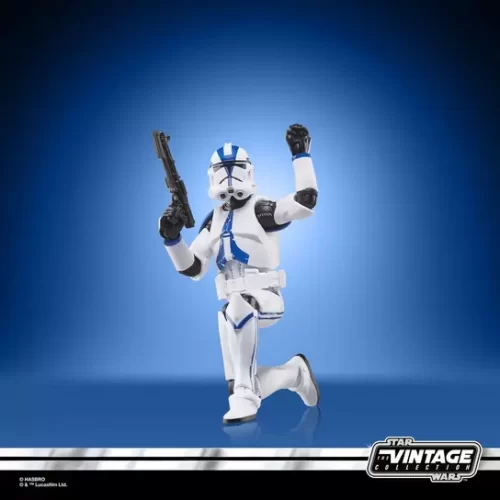
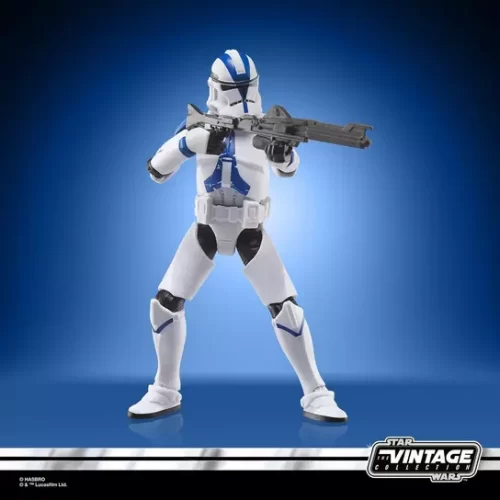
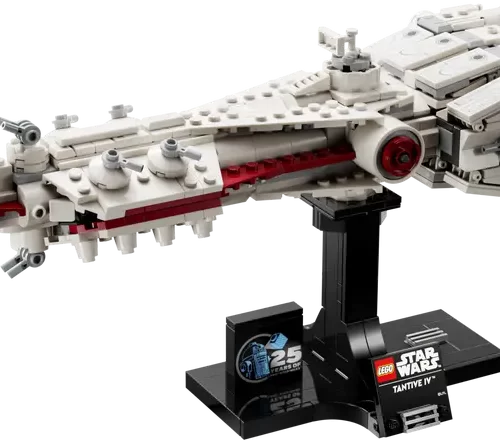
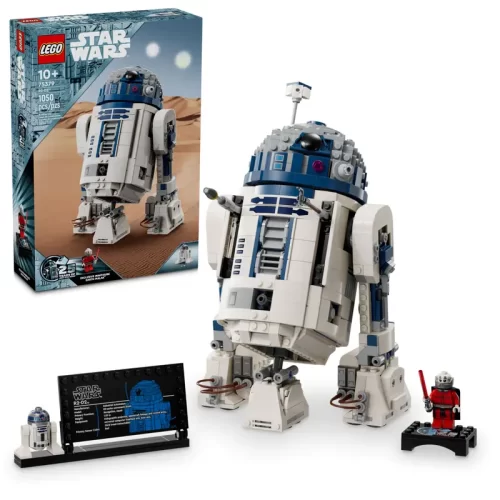
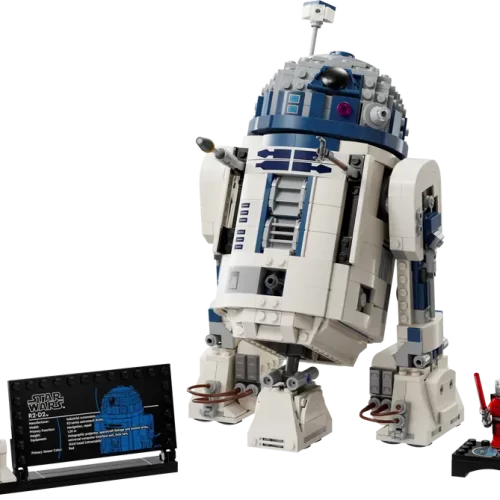
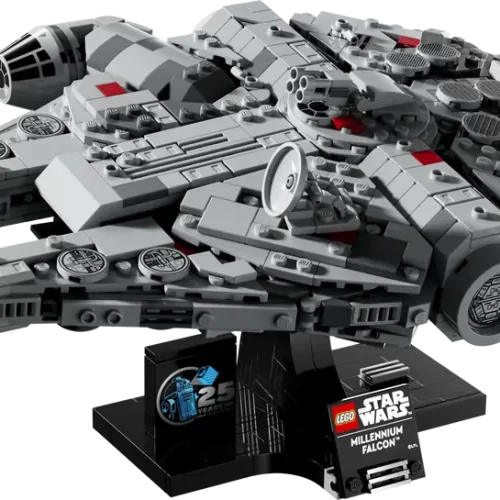
1/1 Scale (2)
1/10 Scale (3)
1/12 Scale (65)
1/18 Scale (27)
1/2 Scale (0)
1/4 Scale (0)
1/6 Scale (0)
1/9 Scale (0)
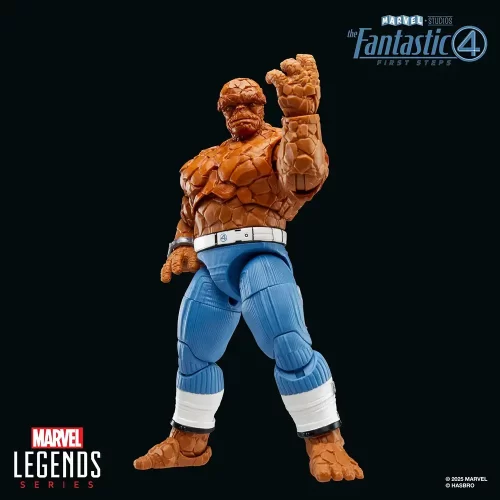
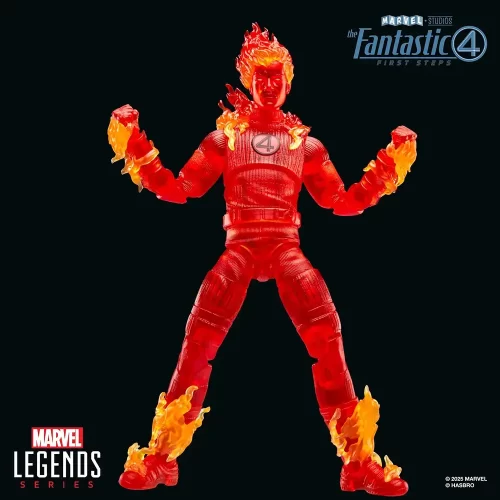
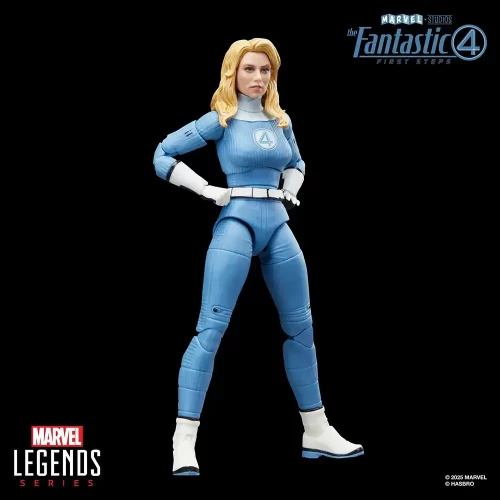
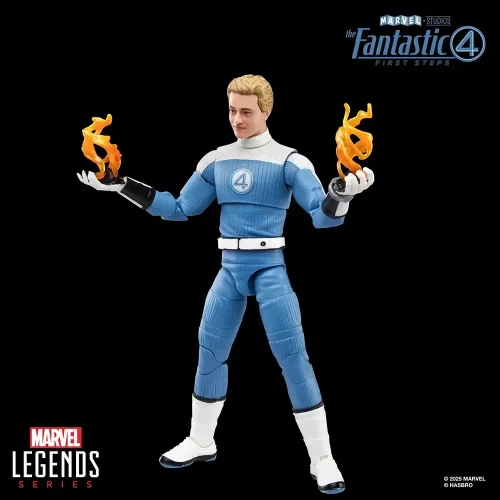
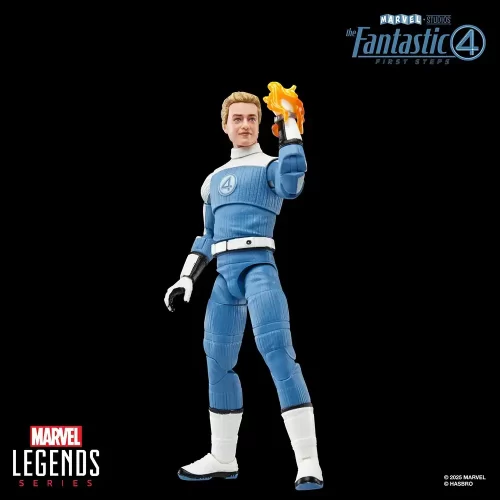
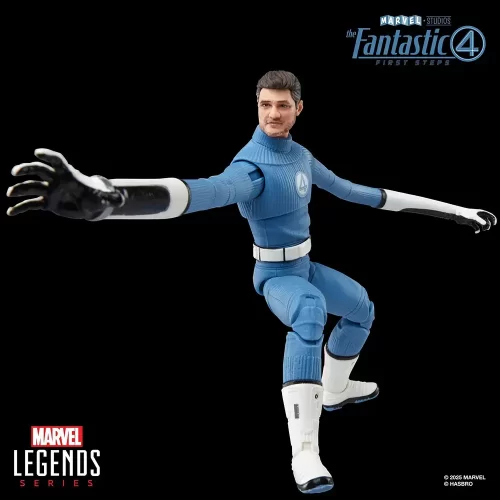
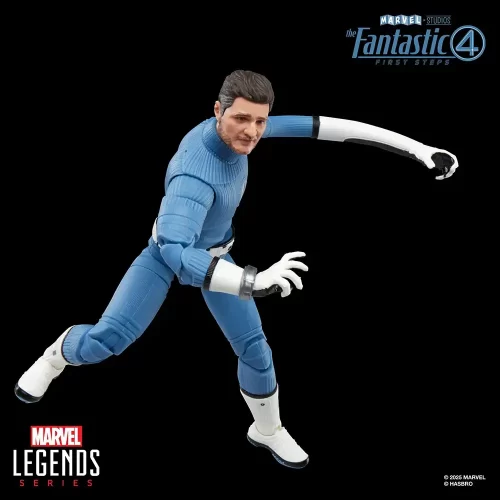
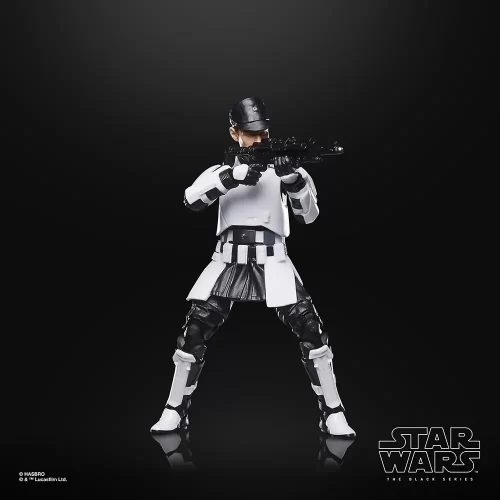
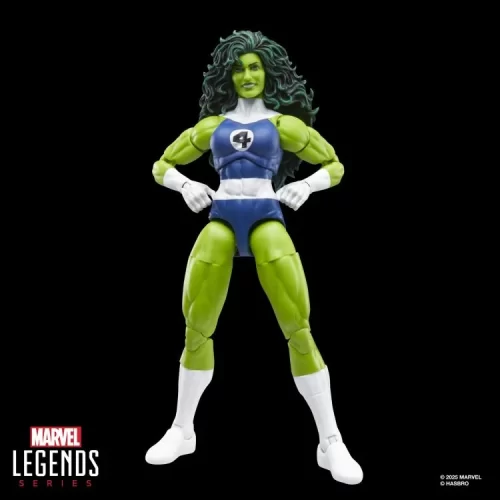
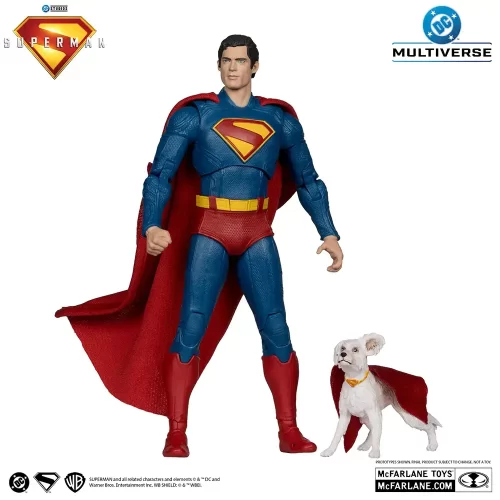
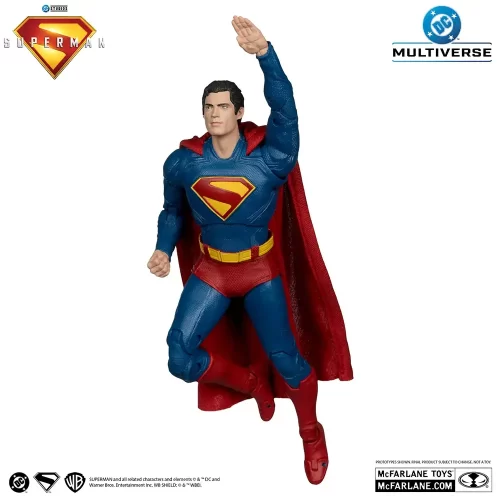
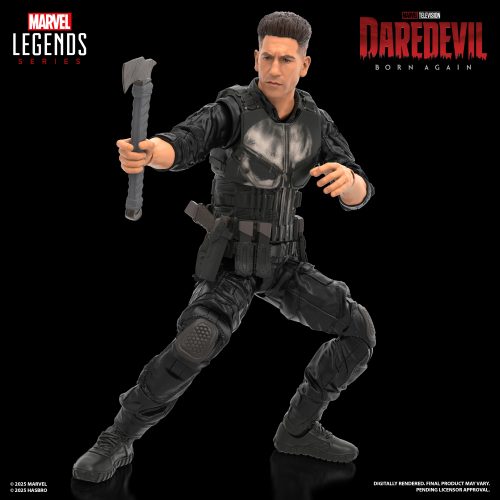
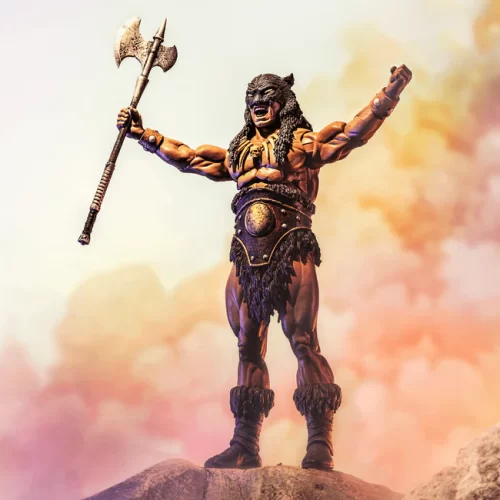
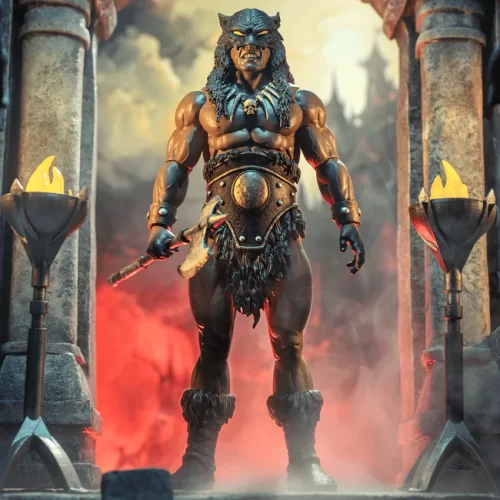
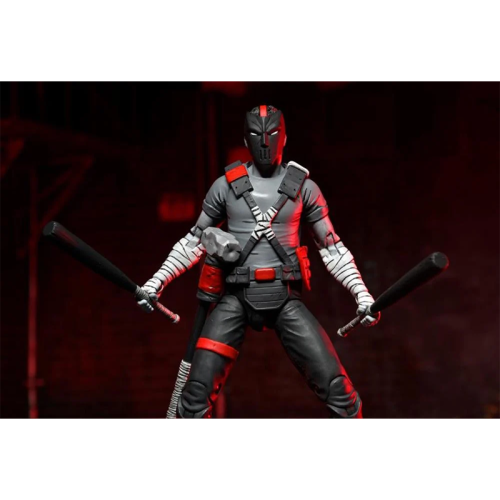
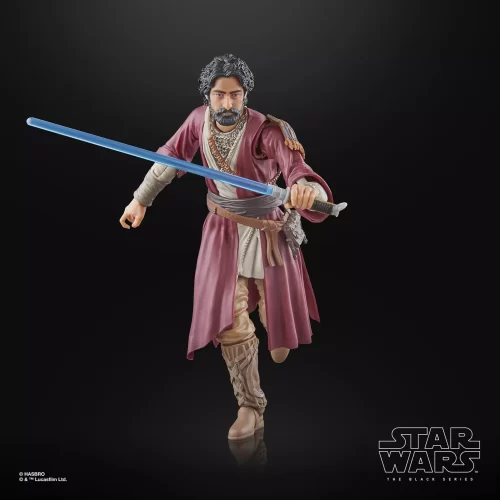
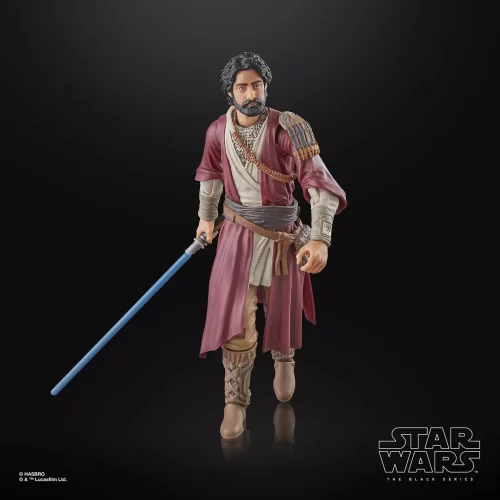
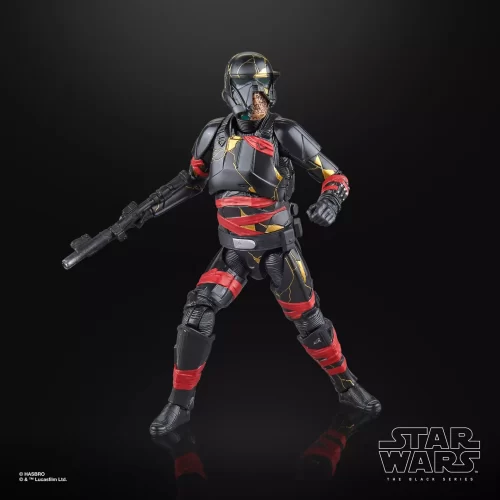
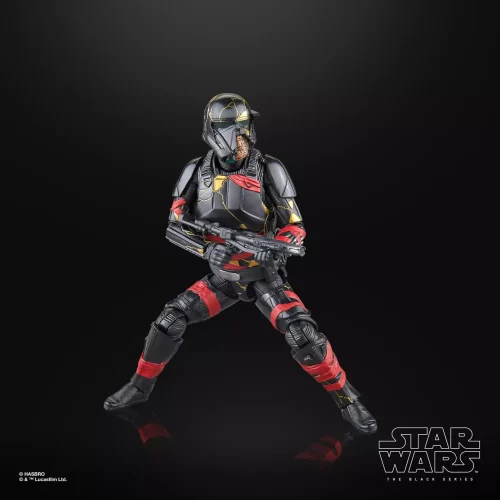
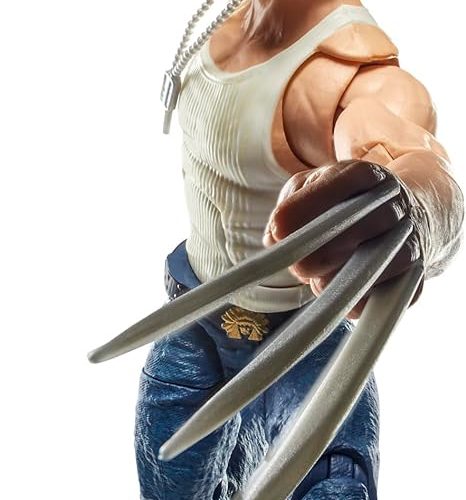
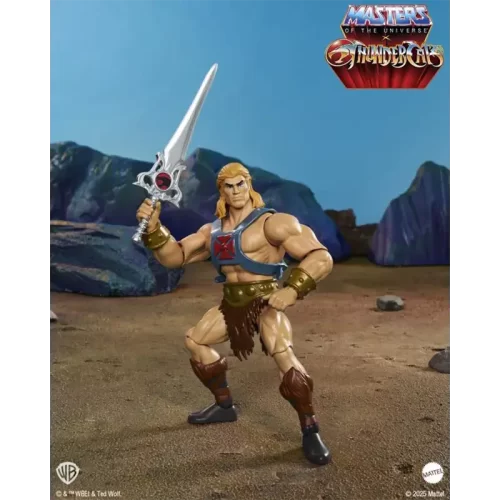
Action Figure (102)
Building Set (15)
Bust (0)
EPIC H.A.C.K.S. (1)
Frazetta Girls (3)
Mattel (7)
NECA (2)
Playset (0)
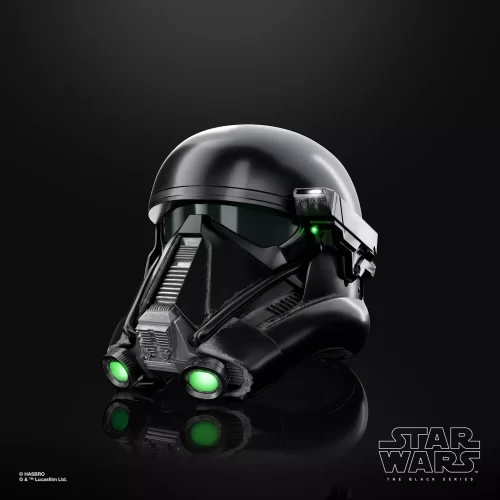
Prop Replica (2)
ReAction (2)
Roleplay (2)
Statue (0)
Super7 (2)
Uncategorized (0)
Vehicle (2)
New (5)
Deals (1)
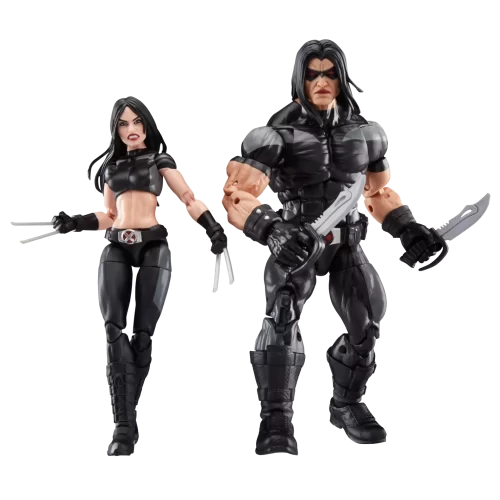
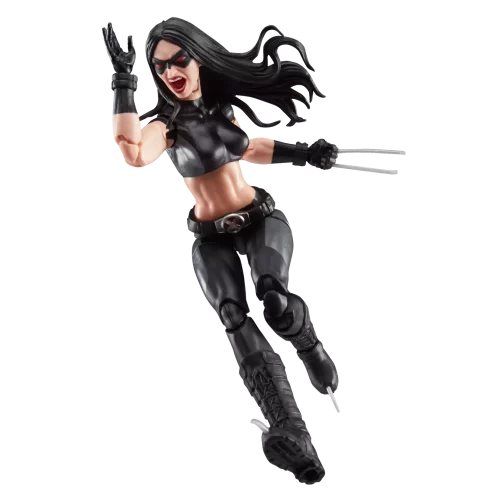
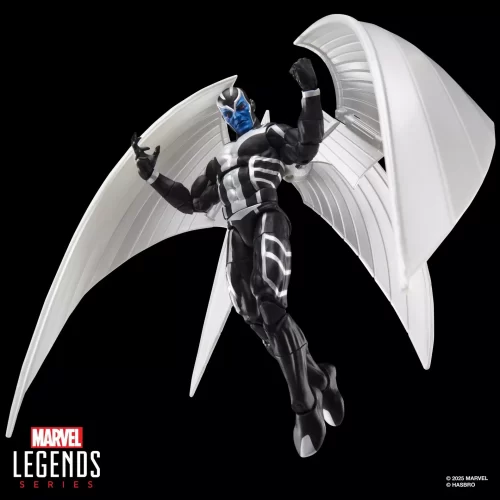
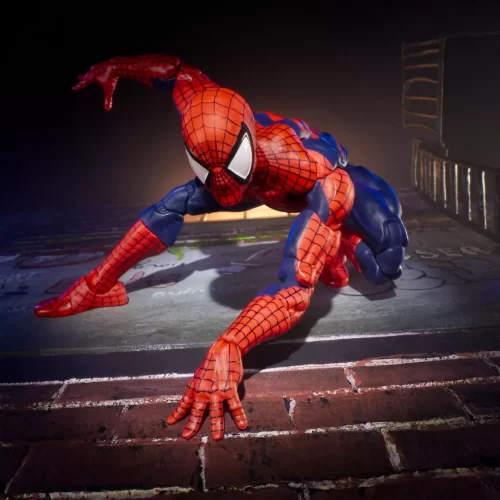
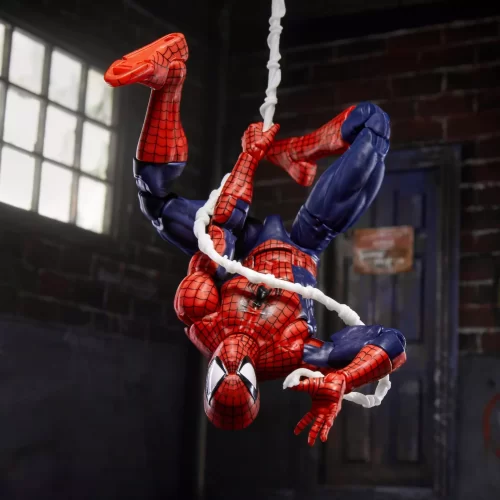
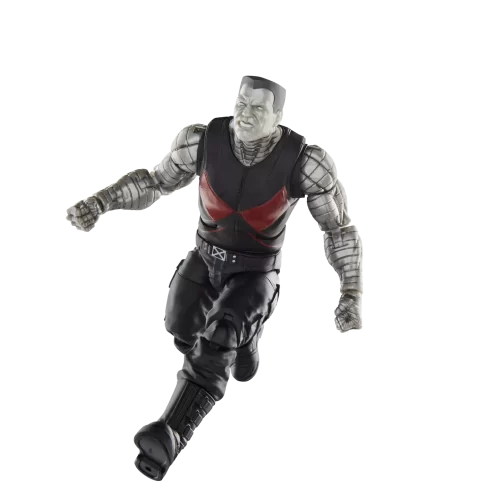
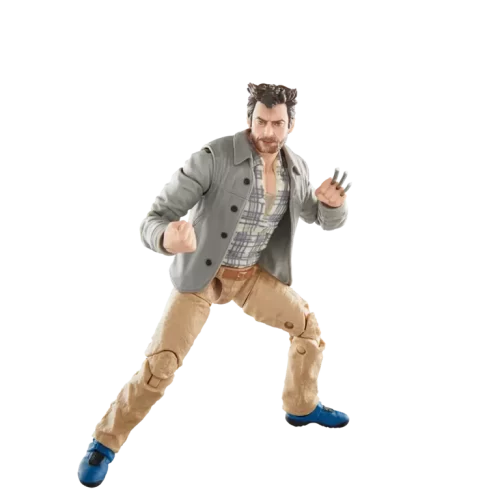
Marvel Legends (32)
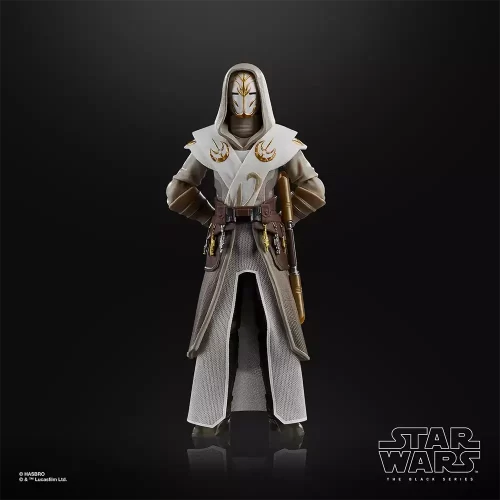
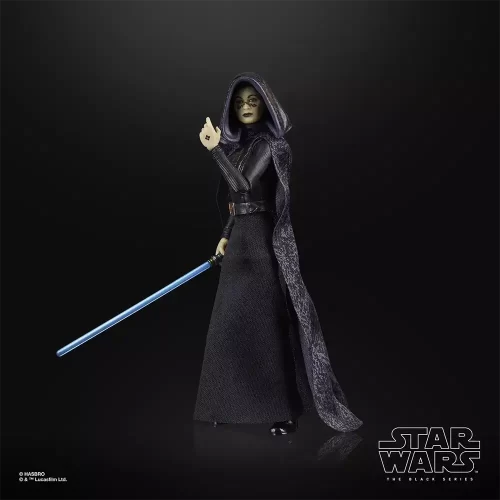
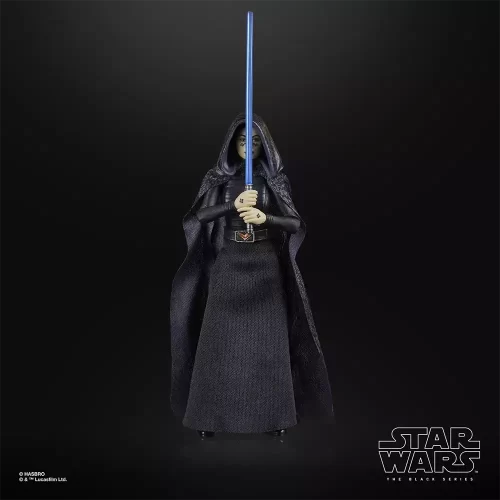
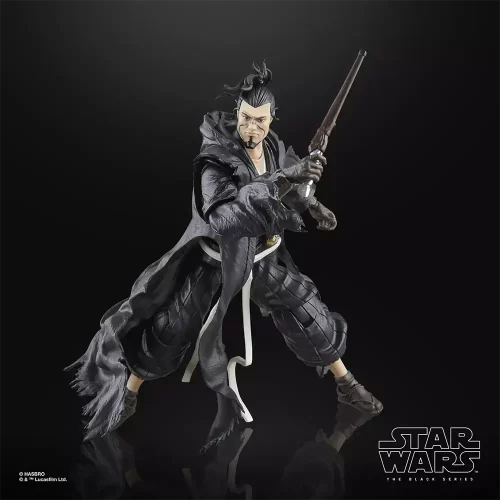
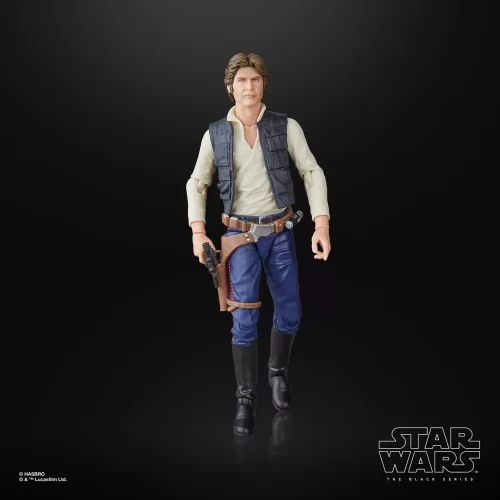
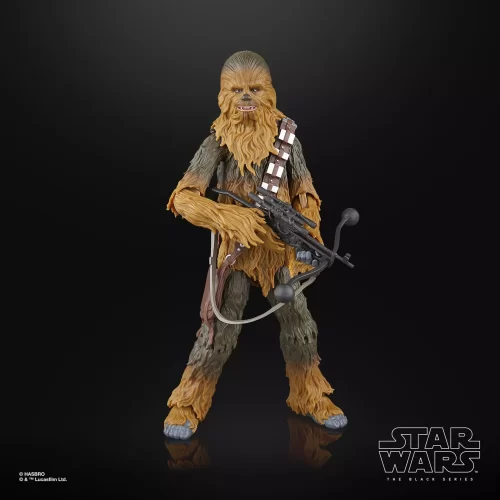
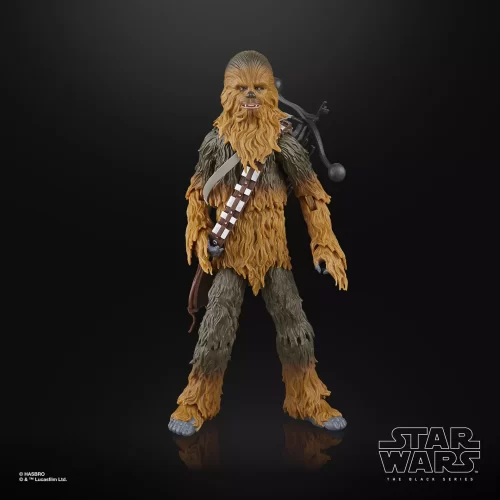
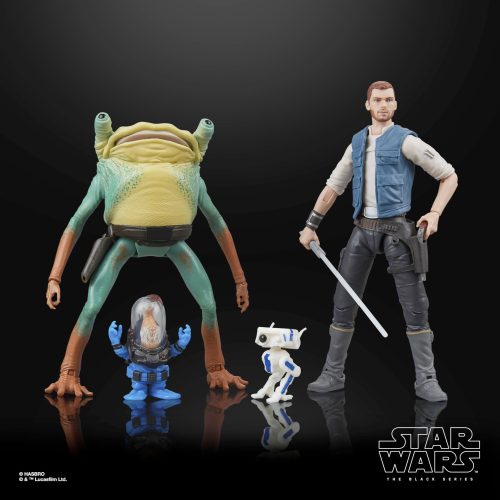
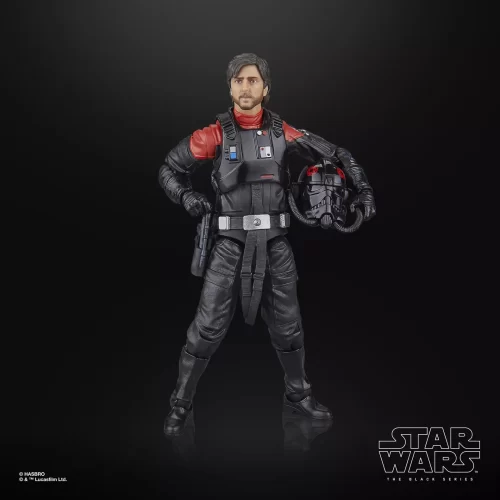
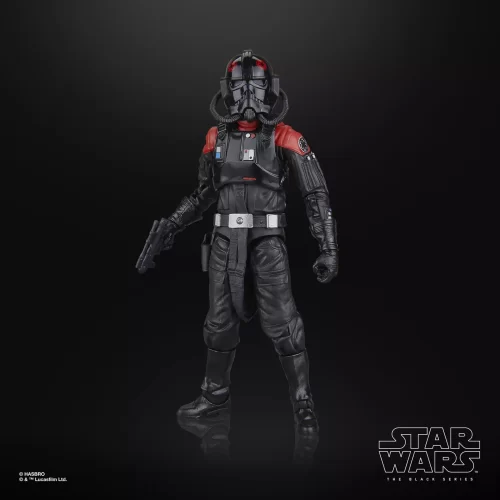
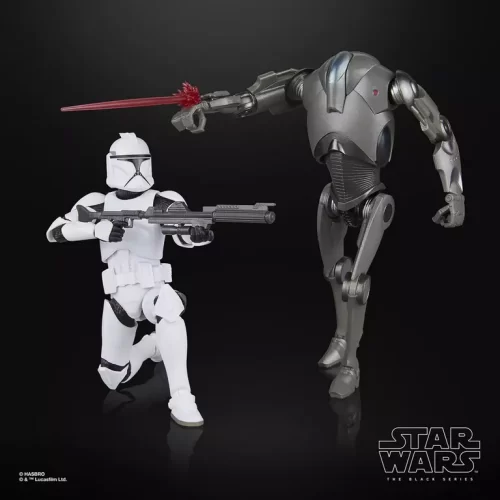
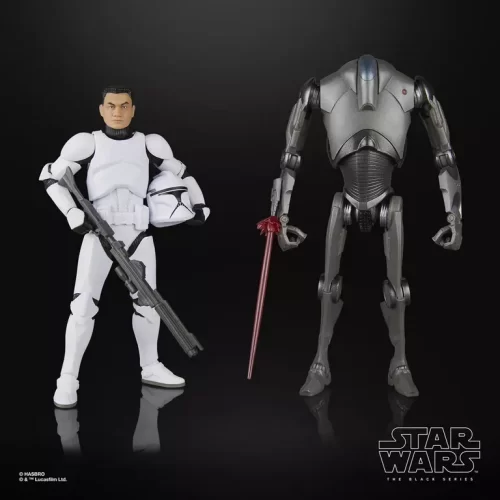
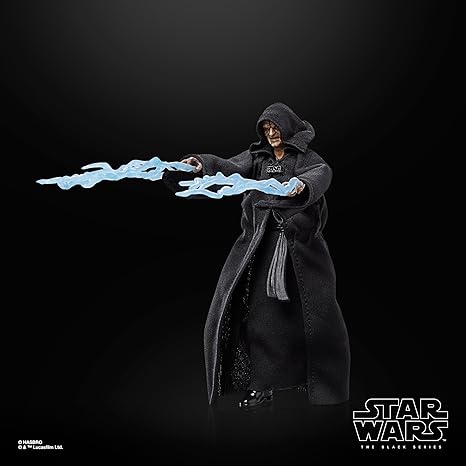
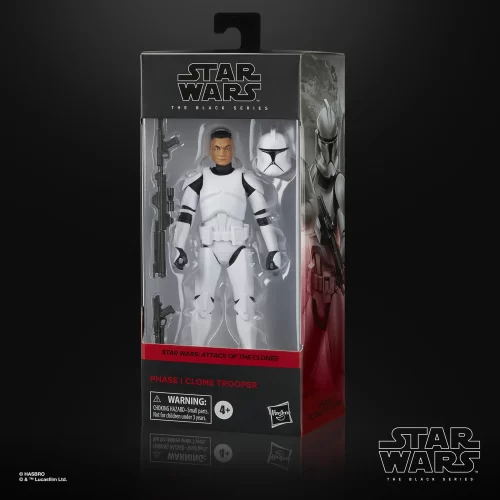
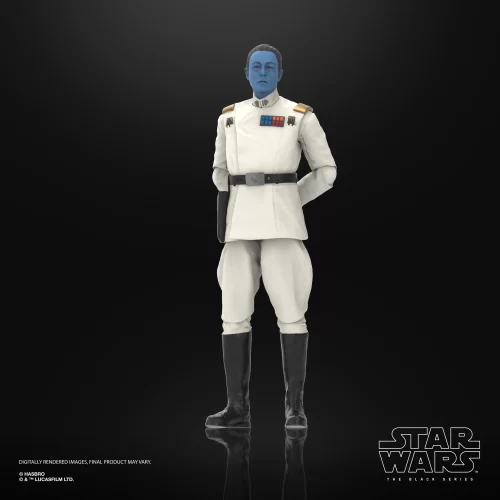
Black Series (31)
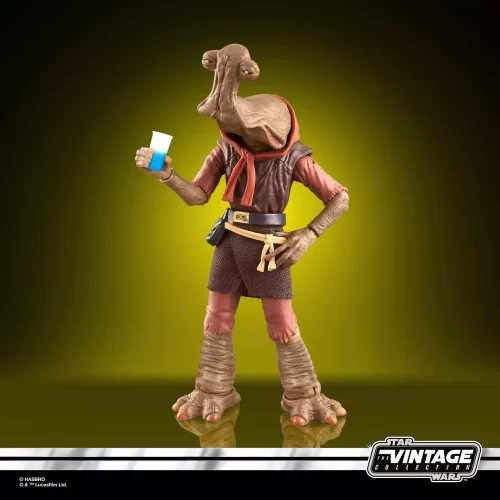
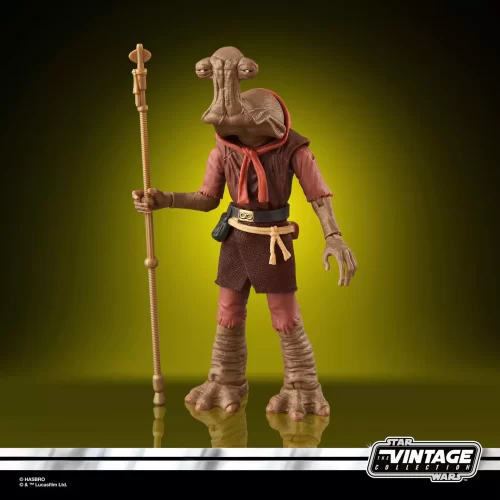
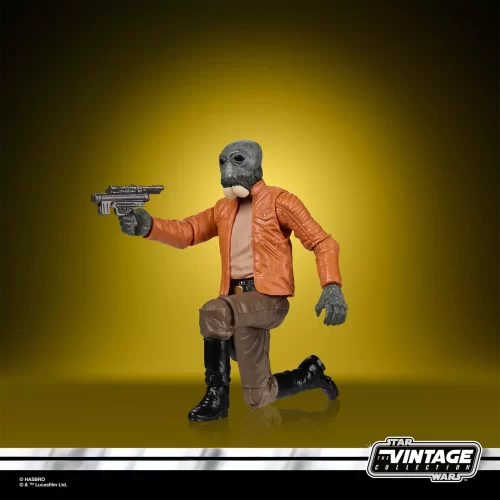
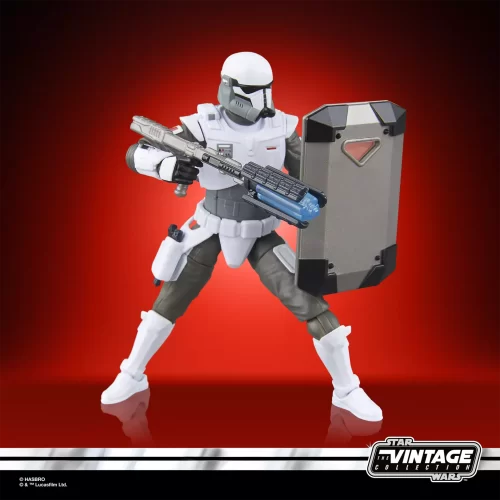
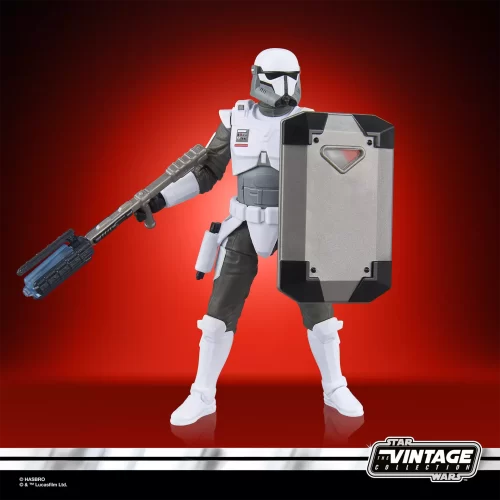
Vintage Collection (25)
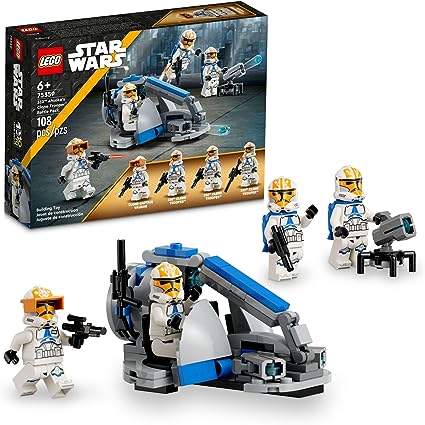
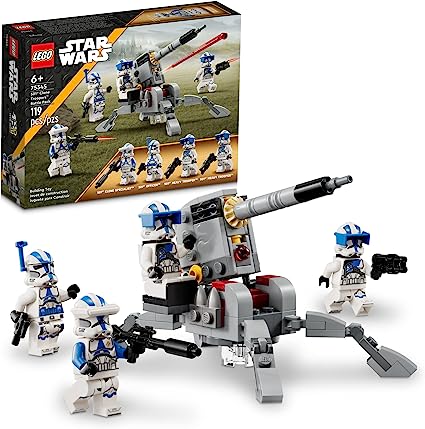
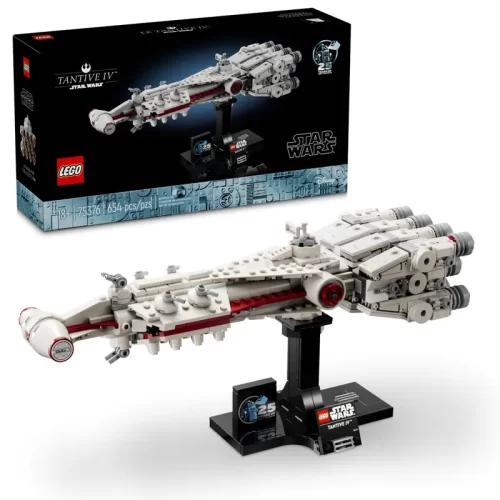
Lego (16)
Hasbro (85)